
Not sure how to pronounce oligohydramnios? Click here. ( oligo = little, hydr = water, amnios = membrane around the fetus, or amniotic sac). Oligohydramnios means low fluid inside the amniotic sac. 2009).īut what is the evidence for this standard birth practice? Let's take a look at the evidence together. In fact, 95% of physicians who practice maternal-fetal medicine feel that isolated oligohydramnios - low amniotic fluid in an otherwise healthy pregnancy - is an indication for labor induction at 40 weeks ( Schwartz, Sweeting et al. is to induce labor at term if a mother has low amniotic fluid in an otherwise healthy pregnancy. This is a great question and I felt like it was a perfect topic for my first article for Science and Sensibility. I'm also curious about causes of low fluid (theorized or known), risks of low fluid, and perhaps as important if not more so, measurements of low fluid.' What does the research say about low fluid at or near term? From what I've been able to see in research summaries at least, there appears to be no improved outcome for babies, but I'd love to see the research really hashed out. 'Low fluid seems to be the new 'big baby' for pushing for induction. This question came from one of my readers: I look forward to future posts and collaboration with Rebecca and thank her for her contribution today.- SM Look for an interview with Rebecca in an upcoming post where we will learn how this Assistant Professor of Nursing who teaches pathopharmacology and studies depression in patients with heart failure ended up writing the Evidence Based Birth blog appreciated by birth professionals. The authors stated that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.Today's post on the Evidence for Induction for Low Amniotic Fluid in a Healthy Pregnancy is a guest post by blogger Rebecca Dekker, owner of the fairly new blog in the birth world, Evidence Based Birth that has been very well received and enjoyed by many. Intraobserver reliability of amniotic fluid volume estimation by two techniques: amniotic fluid index vs. Amniotic fluid volume assessment with the four-quadrant technique at 36–42 weeks’ gestation. Phelan JP, Smith CV, Broussard P, Small M. O Significado da Raça na Sociedade Brasileira.

The amniotic fluid index in normal human pregnancy. The development human: clinically oriented embryology, 4th ed.
Amniotic fluid and maternal characteristics in Chinese pregnancies dated by early ultrasound biometry. Curve of amniotic fluid index measurements in low-risk pregnancy. Machado MR, Cecatti JG, Krupa F, Faundes A. Amniotic fluid index in normal pregnancy: an assessment of gestation specific reference values among Indian women. Khadilkar SS, Desai SS, Tayade SM, Purandare CN. Informações Socioambientais e Geoprocessamento. A longitudinal study of amniotic fluid index in normal pregnancy in Nigerian women. Normal amniotic fluid volume changes throughout pregnancy. Is a normally functioning gastrointestinal tract necessary for normal growth in late gestation? Pediatr Surg Int. Blakelock R, Upadhyay V, Kimble R, Pease P, Kolbe A, Harding J. As Características gerais da população, religião e pessoas com deficiência do Censo Demográfico 2010. Assessment of amniotic fluid index in normal pregnancy at a tertiary care hospital setting.
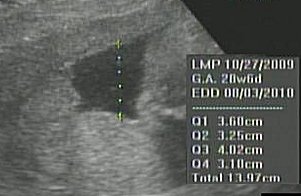
This reference range can be used to monitor deviations in the volume of amniotic fluid in fetuses at high risk for intrauterine growth disturbances. The correlation between AFI and GA was best represented by a linear equation: AFI=17.78–0.153*GA ( R 2=0.027).Ĭonclusion: We established the reference range for the AFI in a large sample of the Brazilian population. The mean AFI ranged from 12.2☒.6 cm at 18 weeks to 11.6☖.0 cm at 38 weeks of pregnancy. Results: The mean maternal age and gestational age were 27.01☖.57 years and 30.43±5.29 weeks, respectively. To assess the correlation between AFI and gestational age (GA), polynomial equations were calculated, with adjustments using the determination coefficient ( R 2). The AFI was measured from the largest vertical pockets of amniotic fluid in the four quadrants of the uterine cavity. Methods: This was a retrospective cross-sectional study on 3837 normal singleton pregnancies between 18+0 and 38+6 weeks of pregnancy. Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the reference range for amniotic fluid index (AFI) measurements in a large sample of the Brazilian population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
